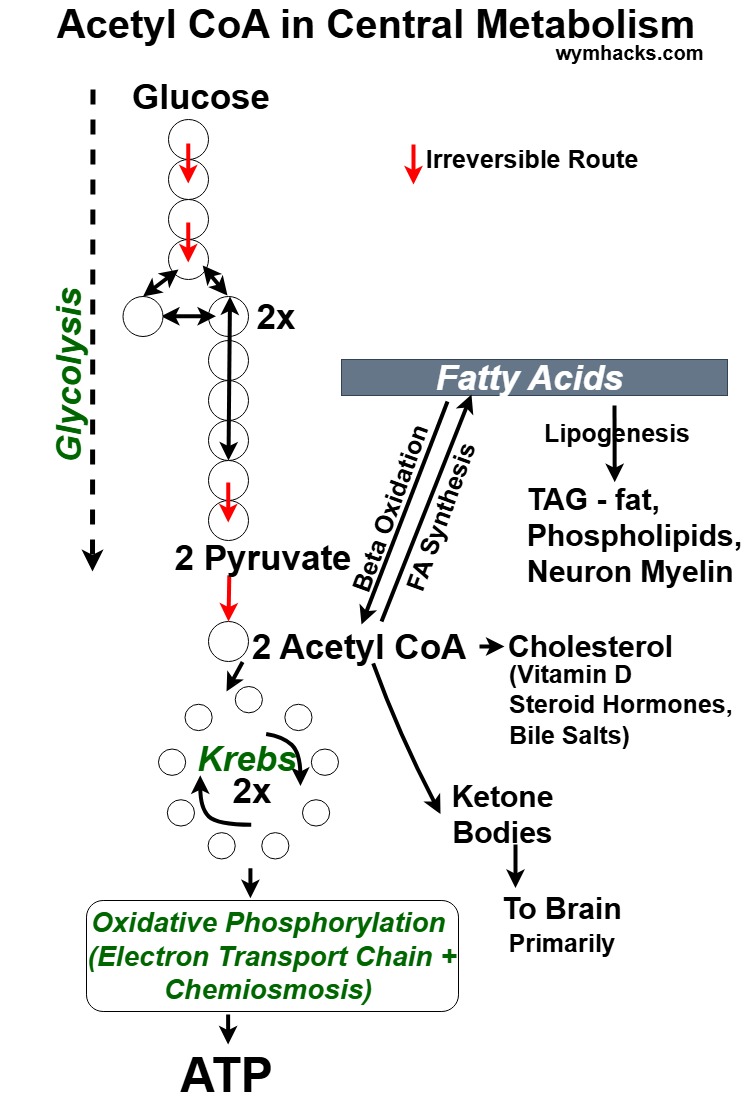
Acetyl CoA Metabolic Routes
Acetyl CoA Metabolic Routes Chart
Last Update: November 3, 2024
Picture_Acetyl CoA Metabolic Routes from Central Metabolism Hub
Note: The following text (in quotations below) was generated with Google Gemini:
Acetyl CoA and Fatty Acids
“Fatty acids, the building blocks of lipids, undergo a dynamic cycle of breakdown and synthesis.
In fatty acid oxidation, long-chain fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon units of acetyl-CoA through a process called beta-oxidation.
- This process occurs in the mitochondria and generates energy in the form of ATP.
Conversely, fatty acid synthesis involves the conversion of acetyl-CoA into fatty acids.
- This process takes place in the cytoplasm and requires energy in the form of NADPH.
The newly synthesized fatty acids can be used for various purposes:
- Triacylglycerol (TAG) synthesis: Fatty acids combine with glycerol to form triglycerides, the primary storage form of energy in the body.
- Phospholipid synthesis: Fatty acids are essential components of phospholipids, which are major constituents of cell membranes.
- Myelin sheath formation: Fatty acids, particularly long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, are crucial for the formation and maintenance of the myelin sheath, a protective layer around nerve cells.”
Acetyl CoA and Cholesterol
“Acetyl-CoA, …, is the building block for cholesterol.
Through a complex series of reactions, it is converted into cholesterol, a vital molecule for various cellular functions.
Cholesterol serves as a precursor for several essential substances:
- Vitamin D: Upon exposure to sunlight, cholesterol in the skin is converted into vitamin D, which plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and bone health.
- Steroid Hormones: Cholesterol is the starting material for the synthesis of steroid hormones, including estrogen, testosterone, cortisol, and aldosterone.
- These hormones regulate various physiological processes, such as reproduction, stress response, and electrolyte balance.
- Bile Acids: Cholesterol is converted into bile acids in the liver, which aid in the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine.”
Acetyl CoA and Ketone Bodies
“Acetyl-CoA, …, can be converted into ketone bodies during periods of low glucose availability, such as fasting or prolonged exercise.
This process, known as ketogenesis, primarily occurs in the liver.
Ketone bodies, including acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone, are water-soluble and can be transported through the bloodstream to tissues like the brain and heart.
- These tissues can utilize ketone bodies as an alternative energy source, especially when glucose levels are low.
- Ketone bodies are particularly important for the brain, which has limited capacity to use fatty acids directly as fuel.”
Note: The following text (in quotations above) was generated with Google Gemini.
Disclaimer: The content of this article is intended for general informational and recreational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional “advice”. We are not responsible for your decisions and actions. Refer to our Disclaimer Page.