Menu (linked Index)
Electricity (9/11) – AC Theory
Last Update: January 15, 2026
Introduction
This is the ninth installment in a series of posts on electricity.
This installment serves as a central hub for four key modules (posts) covering the mathematical and physical foundations of Alternating Current.
The main topics covered are:
- Circuit Analysis Math: A refresher on using Trigonometry, Complex Numbers, and Euler’s Equation ( ejθ = cos(θ) + jsin(θ) ) to simplify sinusoidal analysis.
- Voltage & Current: Defining instantaneous values using sine waves and phasors.
- I-V (Current – Voltage) Relationships: Calculating Impedance (Z) and Admittance (Y) to determine how components resist or assist AC flow.
- Power Equations: Breaking down the Power Triangle: Real (P), Reactive (Q), and Apparent (S) power.
Navigation Index to Electrical Series Posts
Navigate to other posts in this series from the linked index below.
Electricity_(1/11 ) Introduction
Electricity_(2/11 ) Mathematical Foundations
Electricity_(3/11) Motion and Force
Electricity_(4/11) Energy, Work, and Power
Electricity_(5/11) Electrostatics, Current and Voltage
Electricity_(6/11) Electric Field, Magnetic Field, Current, And Voltage Relationships
Electricity_(7/11) Circuits, Resistors, Inductors, and Capacitors
Electricity_(9/11) AC Theory
Electricity_(10/11) Power Systems and the Grid
Electricity_(11/11) Timeline of Key Developments in Electromagnetism
On Line References
Listen, I could have easily listed 100 good references here.
There are indeed many on line references linked in many of my posts.
Here are a few I figured you should definitely have at your fingertips.
The first two are just good references for you to keep your units of measure straight.
The khanacademy.org link houses probably the greatest collection of STEM related videos, taught by several amazing teachers.
Finally, my “best of teachers” listing , gives you a certainly incomplete list of some amazing teachers that post their videos for free on the web.
- Symbols, Units, Nomenclature and Fundamental Constants in Physics – IUPAP 2010 – by Cohen and Giacomo
- NIST Office of Weights and Measures: www.NIST.gov SI units
- https://www.khanacademy.org/
- The Best On-Line Teachers
Circuit Analysis Math Basics: Trig, Complex Numbers, and Euler’s Equation
Summary of the Contents (Link to the full posting via the link above or at the bottom of this section)
You need a little math refresher.
This post explores the basic math that underpins the modeling of alternating current (AC) circuits.
We begin with the basic geometric ratios of right-triangle trigonometry and extend these concepts using the unit circle to define trigonometric functions for all angles.
We then introduce complex numbers and the geometric rotation property of the imaginary unit j to reveal a powerful mathematical tool: Euler’s formula.
This formula allows us to represent time-varying sinusoidal waveforms (like current and voltage) as simple rotating vectors on the complex plane, providing the essential framework used by engineers to analyze and solve complex electrical systems.
Please access the full post through this link → Circuit Analysis Math Basics: Trig, Complex Numbers, and Euler’s Equation
AC Voltage and Current Equations
Summary of the Contents (Link to the full posting via the link above or at the bottom of this section)
A three-phase power generator creates electricity by
- rotating a powerful magnet (the rotor)
- inside a stationary frame containing three separate sets of wire coils (the stator),
- each spaced 120 degrees apart .
Picture: Simplified Three Phase AC Generator
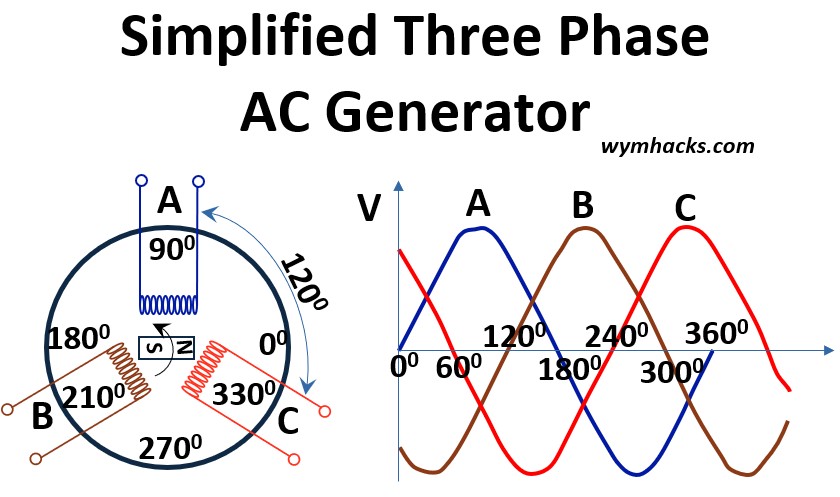
As the magnet spins, its magnetic field sweeps across the coils, inducing a voltage in each one, a principle known as electromagnetic induction.
Because the coils are physically spaced 120 degrees apart, the voltage waveform produced in each coil is also out of phase by 120 degrees from the others.
This process simultaneously generates three distinct AC voltages of the same frequency and amplitude, which are then transmitted to produce the highly efficient and constant power delivery characteristic of three-phase power .
To fully understand the precise relationship between the spinning magnet and the generated electricity, this article derives the mathematical equation that formally defines the periodic, sinusoidal shape of each of these three voltage waveforms.
This equation is essential for modeling and analyzing all aspects of AC power generation.
Please access the article through this link → AC Voltage and Current Equations
AC Circuits: I-V Relationships, Impedance, Admittance, and Power
Summary of the Contents (Link to the full posting via the link above or at the bottom of this section)
This article explains Alternating Current (AC) circuit fundamentals, beginning with the distinct i-v relationships of simple resistor (R), inductor (L), and capacitor (C) circuits.
We establish the mathematical foundation for each element in the time domain, detailing how resistors dissipate energy while inductors and capacitors store and release it through magnetic and electric fields.
Pictures: Simple (Pure) Resistor, Inductor, and Capacitor AC Circuits
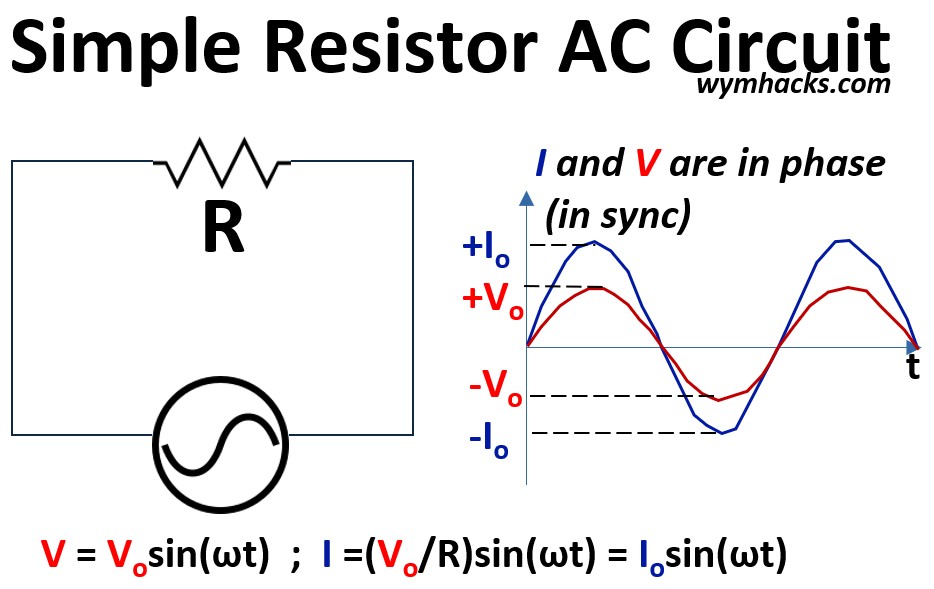
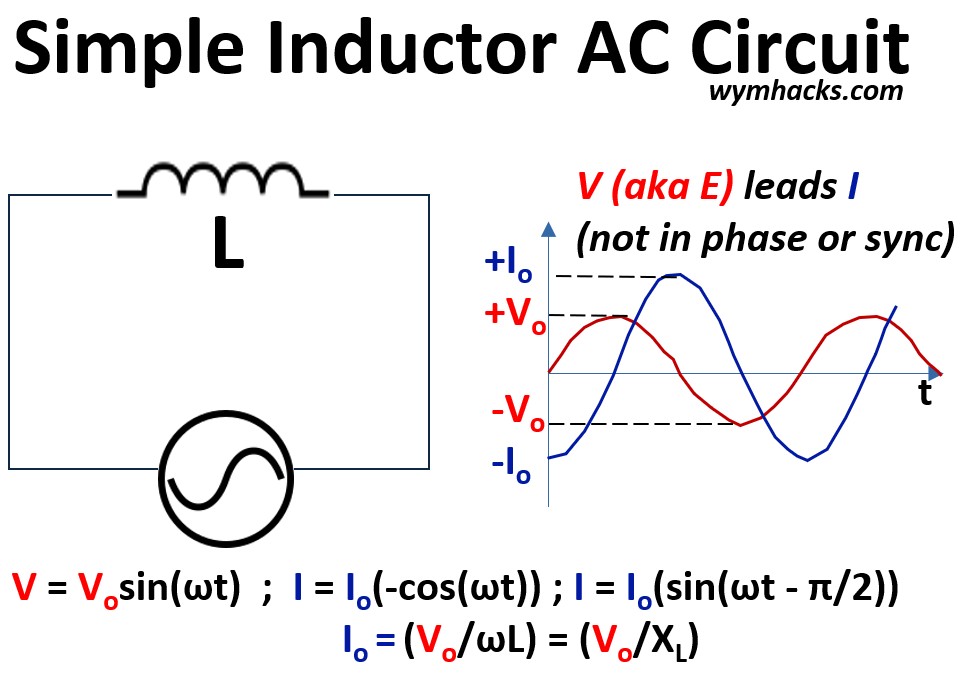
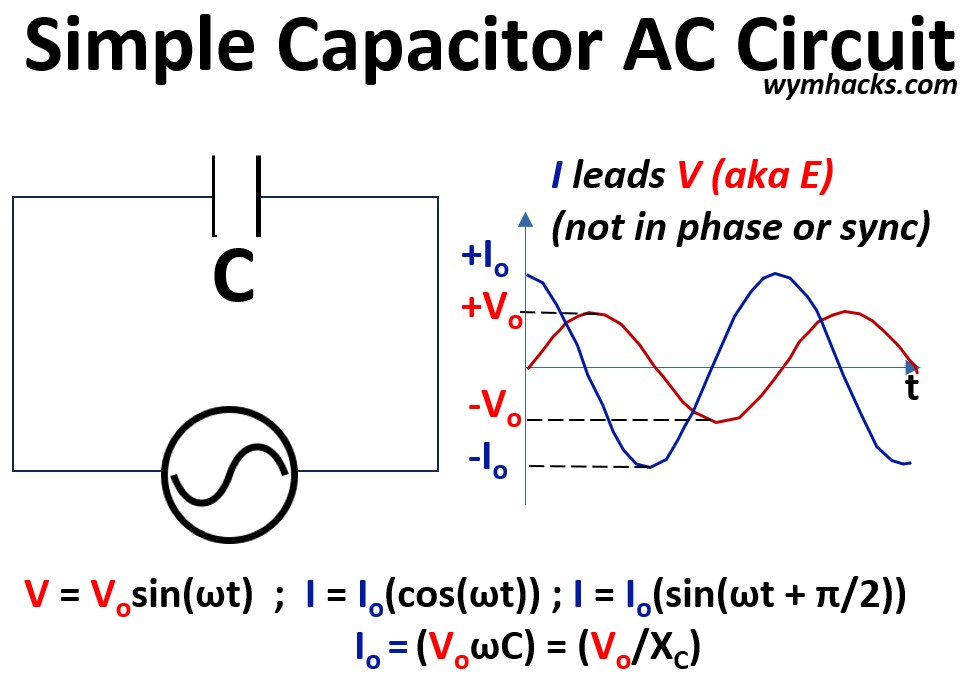
We address the phase shifts inherent to reactive components—where current lags voltage in inductors and leads in capacitors—utilizing the “ELI the ICE man” mnemonic for clarity.
To simplify the analysis of time-varying signals, the guide transitions from time-domain equations to frequency domain equations.
Using Euler’s formula, we introduce phasors and the concept of complex impedance (Z) and admittance (Y).
This transformation allows for the treatment of sinusoidal voltages and currents as rotating vectors, turning complex differential equations into manageable algebraic operations.
The final sections apply these tools to combined RLC circuits in both series and parallel configurations.
Picture: Series and Parallel RLC AC Circuits
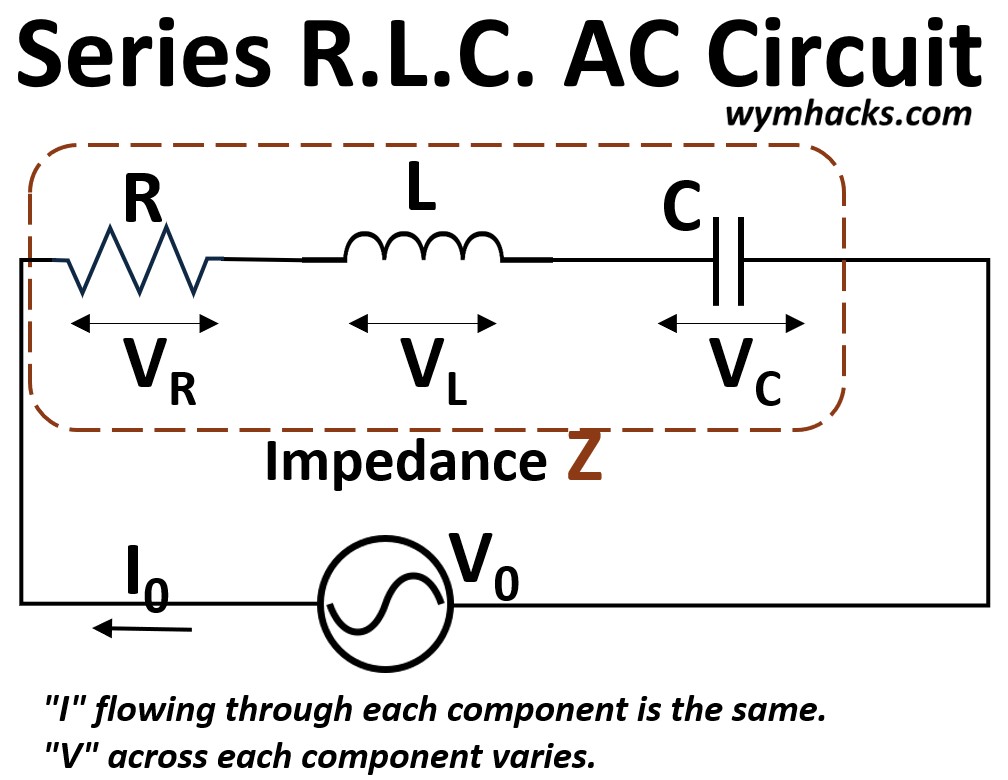
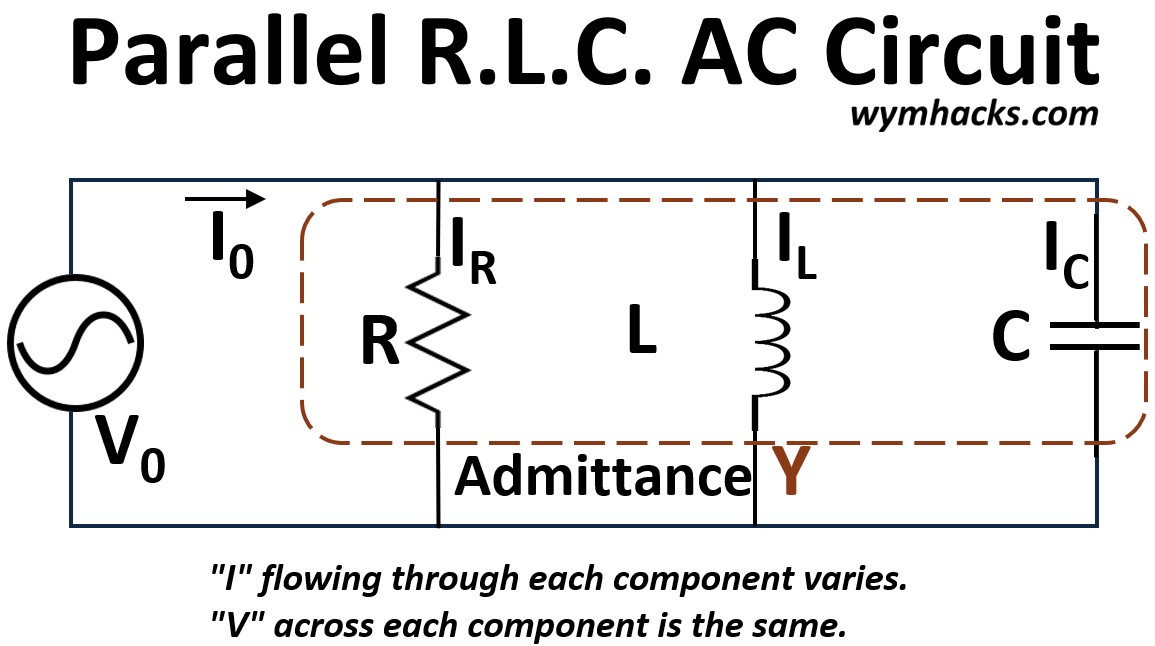
We derive the total circuit response using vector addition, illustrated through voltage, impedance, and power triangles.
Detailed summary tables are provided to bridge the gap between theoretical equations and practical circuit behavior, ensuring a complete understanding of how real power and reactance interact within a system.
Please access the full article through this link → AC Circuits: I-V Relationships, Impedance, Admittance, and Power
Electrical Power Equations
Summary of the Contents (Link to the full posting via the link above or at the bottom of this section)
This post provides a technical breakdown of electrical power, moving from fundamental DC theory to complex three-phase systems.
We begin with the derivation of power equations from Ohm’s Law and progress through the mathematical origins of single-phase and balanced three-phase AC power.
After establishing these algebraic foundations, the focus shifts to the geometric and physical reality of the power triangle.
Picture: Power Triangle: Balanced 3 Phase AC System
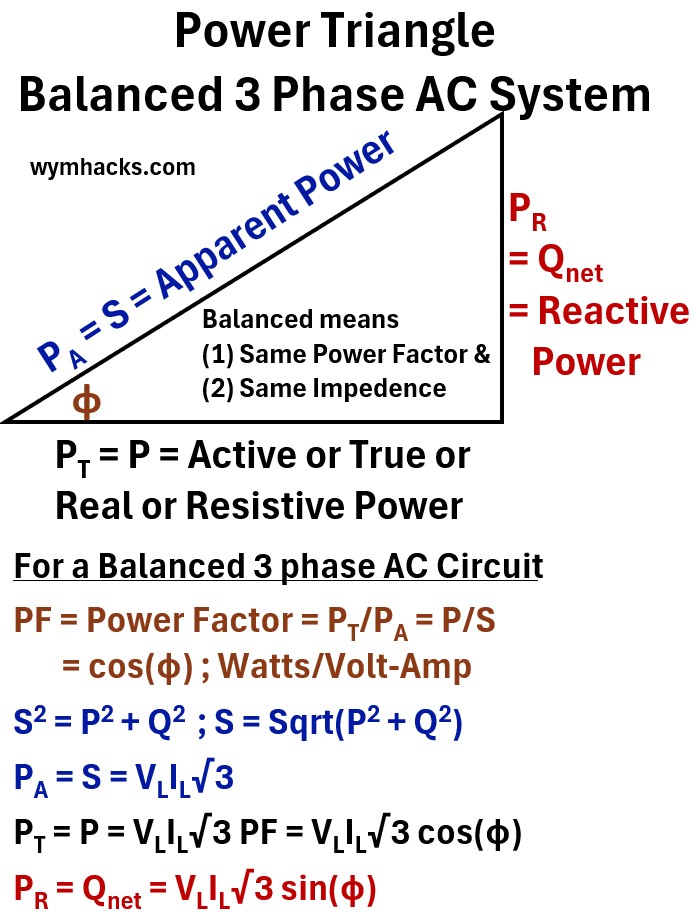
We distinguish between active, reactive, and apparent power—using both the traditional “Beer Analogy” and the more physically accurate “Horse and Railcar” model—before concluding with the methodology required to calculate power in unbalanced systems where standard symmetry fails.
Please access the article through this link →Electrical Power Equations
Disclaimer: The content of this article is intended for general informational and recreational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional “advice”. We are not responsible for your decisions and actions. Refer to our Disclaimer Page.
