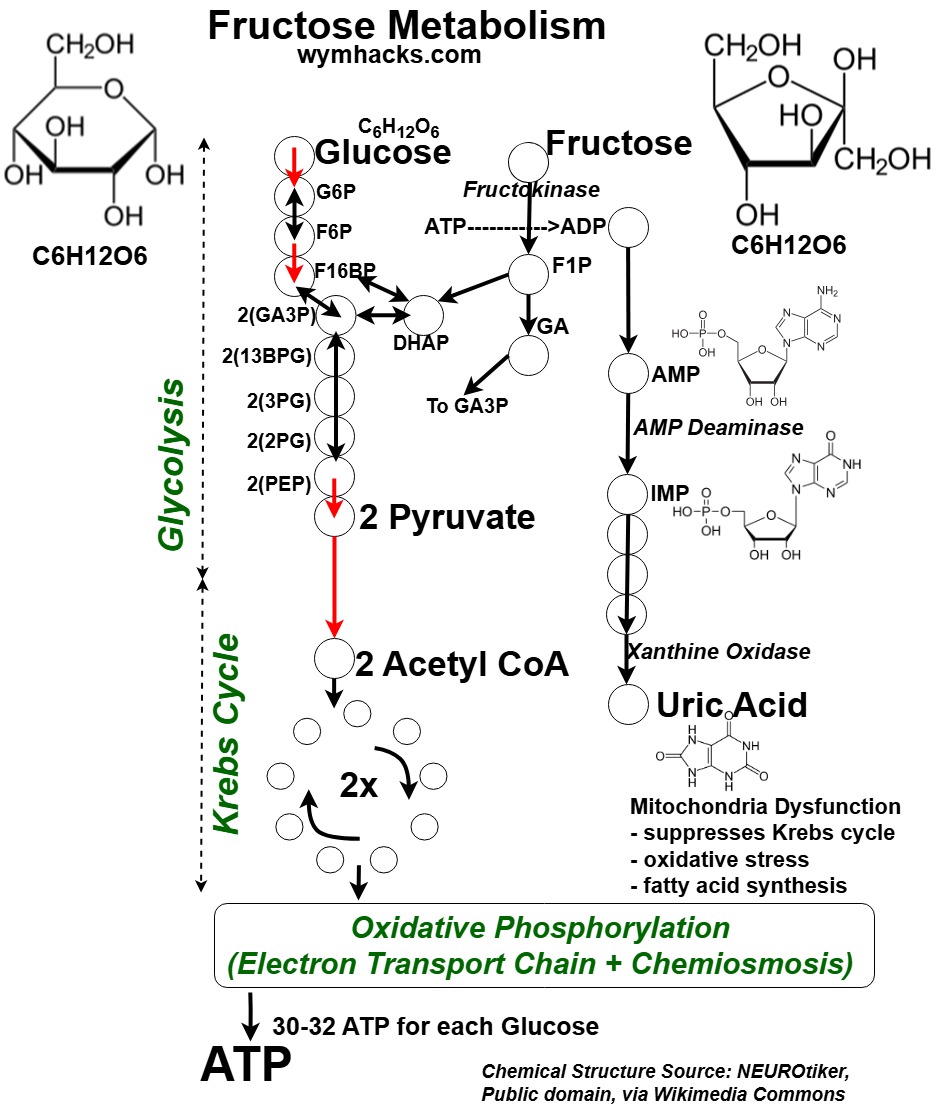
Fructose Metabolic Pathway
Fructose Metabolism Chart
Last Update: November 3, 2024
Picture Fructose Metabolic Routes
Note: The following text (in quotations below) was generated with Google Gemini:
“Fructose_a simple sugar, enters the glycolysis pathway through a unique route that differs from glucose.
- It is first phosphorylated by fructokinase to fructose-1-phosphate (F1P).
- Unlike glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), fructose-1-phosphate bypasses the regulatory steps of glycolysis.
- It is then cleaved by aldolase B into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde (GA).
- DHAP can directly enter glycolysis, while
- glyceraldehyde is phosphorylated to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GA3P), another glycolytic intermediate.”
“However, the rapid metabolism of fructose_can lead to the production of uric acid.
- When_fructose is phosphorylated by fructokinase, ATP is used, resulting in the formation of ADP.
- ADP is further metabolized to AMP, which can be deaminated to uric acid.
- …uric acid can contribute to hyperuricemia, a condition associated with gout and other health problems.”
“Additionally, the rapid entry of fructose_metabolites into glycolysis can overwhelm the liver’s capacity to process them, leading to increased fatty acid synthesis and triglyceride accumulation.
This can contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and other metabolic disorders.”
Note: The following text (in quotations above) was generated with Google Gemini.
Disclaimer: The content of this article is intended for general informational and recreational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional “advice”. We are not responsible for your decisions and actions. Refer to our Disclaimer Page.