Introduction
Electro-Magnetic Radiation
Last Update: October 20, 2024
This post is a brief refresher on Electro-Magnetic Radiation (i.e. light).
See my other posts where light plays a critical role.
- A Color Primer (Including How to Create an Effective Colour Palette)
- Find more links related to my eye research here: Understand Your Eyes.
Electro-Magnetic Radiation
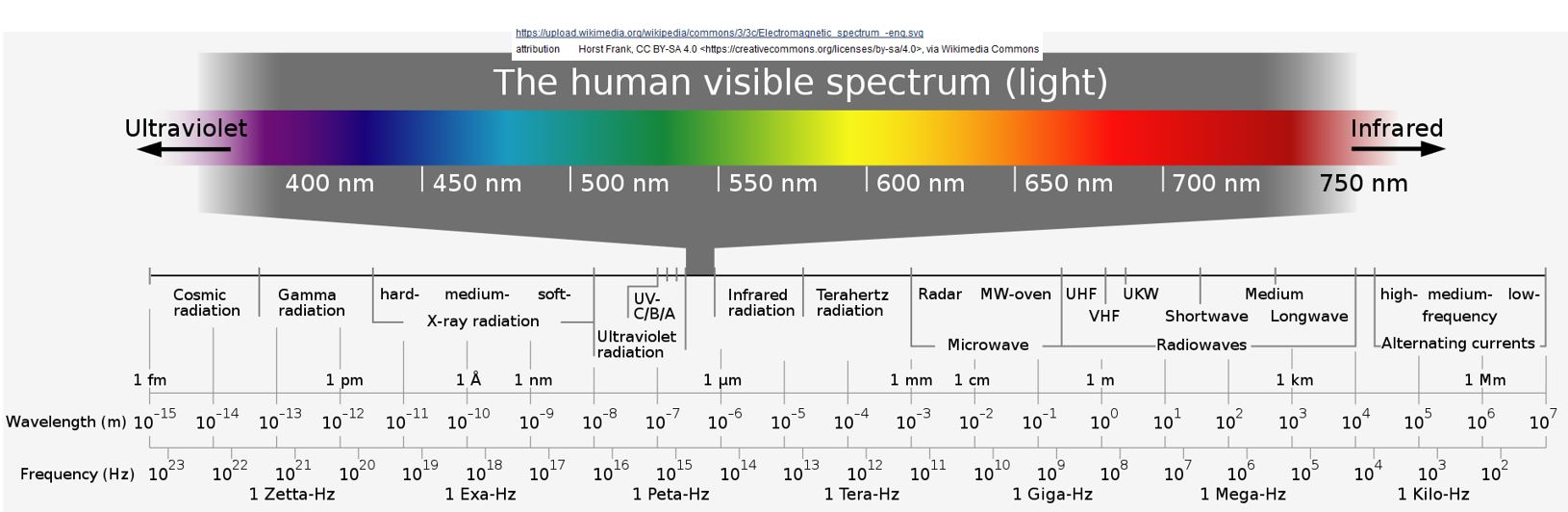
The human visible spectrum of light represents a small section of the full range of light which is called the Electro-Magnetic Spectrum (EMS).
The EMS, in-total, can be described as Electro-Magnetic Radiation (EMR).
In the graphic below you can see that visible light represents only a small portion of the full EMS (ranging from roughly 400 nanometers of wavelength to about 750).
Picture_The Human Visible Spectrum
EMR Has Interesting Characteristics
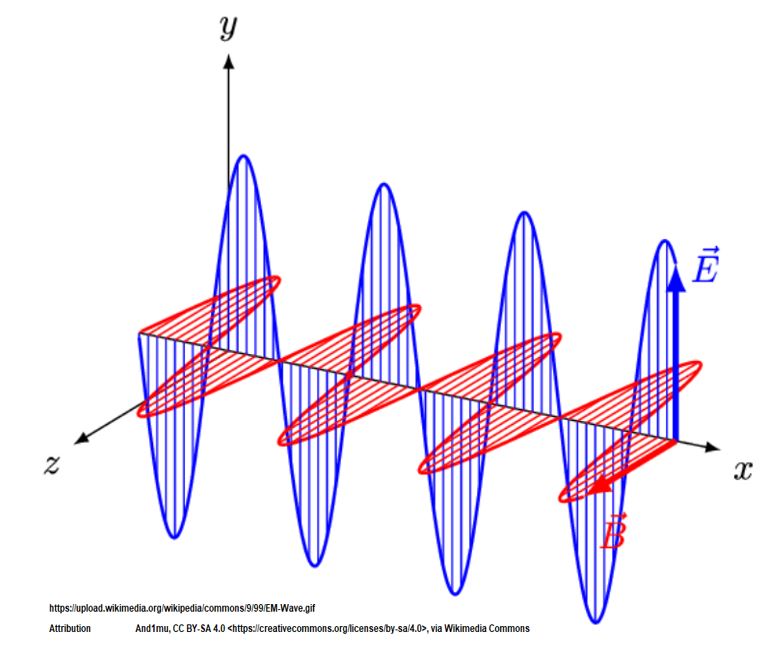
- Electro-Magnetic Radiation, EMR, is radiation energy which travels in the form of electro-magnetic waves.
- EMR is (mathematically) both a wave and a particle (a photon, a massless unit of energy).
- Electro-Magnetic Radiation, EMR, has oscillating electric and magnetic fields
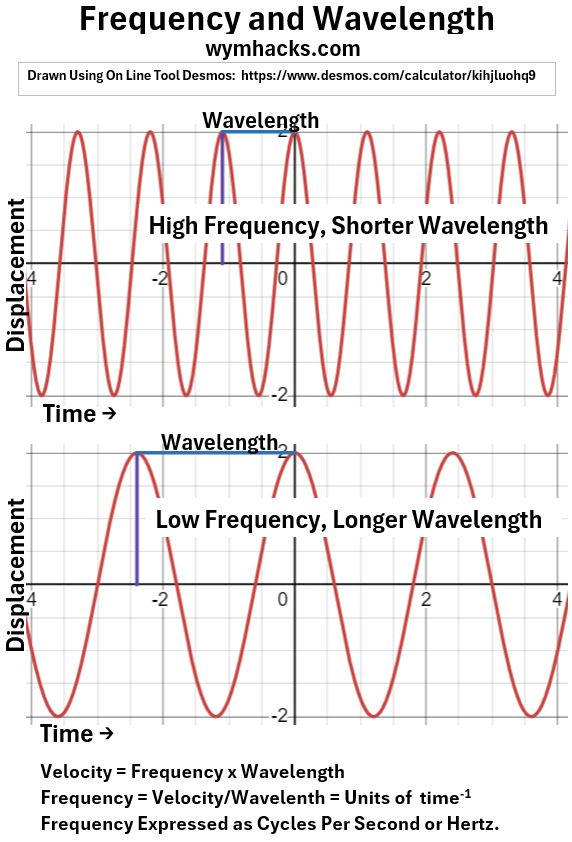
- As a wave, EMR has a wavelength (crest to crest or trough to trough distance) and frequency (number of waves passing a point per unit time).

- These waves can travel through a vacuum (it doesn’t need a medium like sound would for example).
- EMR moves at the speed of light which is super fast (would go around the earth’s equator almost 7.5 times in one second). Nothing can go faster by the way.
- In a vacuum light travels at
- 299,792,458 meters/second
- 670,616,629 miles/hour
- 1,079,252,848.8 kilometers/h
- 186,282 miles/second approximately
- Sunlight is mostly in the Infrared, Visible, and Ultraviolet parts of the electro-magnetic spectrum
- In the 1600s, Isaac Newton demonstrated that sunlight “contains” the visible spectrum by bending (refracting) light and then “recombining” light through a series of two prisms.
- By “contains” we mean: possesses the range of electro-magnetic wavelengths that we see as the rainbow colors.
- Newton probably coined the word Spectrum. It comes from the Latin for ghost , apparition or specter.
- Visible light has wavelengths between 400 and 750 nanometers.
- A nanometer or nm is 1 billionth of a meter.
- In the visible region,
- Violet light has the shortest wavelength (highest frequency) and
- Red light has the longest wavelength (lowest frequency).
- Color doesn’t exist outside our bodies.
- Electro-Magnetic Waves are sensed and translated by our eyes and brains into colour.
- The Scot, James Clerk Maxwell (1831 – 1879), and the German, Heinrich Rudolph Hertz (1857 – 1894), did pioneering work in this area.
Disclaimer: The content of this article is intended for general informational and recreational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional “advice”. We are not responsible for your decisions and actions. Refer to our Disclaimer Page.