Menu (linked Index)
Understanding Your Eyes – A Guide to Anatomy, Vision, and Correction
Last Update: January 10, 2025
Introduction
In the book “The Auto Biography of Malcolm X” , Malcolm writes……”I would just like to study. I mean ranging study, because I have a wide open mind. I’m interested in almost any subject you can mention”.
To use Malcolm’s description , I did a ‘ranging study’ on the eye in order to better understand,
- eye vision impairments (like Cataracts, Near Sightedness, Far Sightedness, Presbyopia and Astigmatism) and
- their correction though eye-wear and surgery.
The result of this effort are my articles listed and linked below.
I’ve organized the articles into four categories
- Anatomy
- Light to vision pathway
- Physics
- Vision impairment and correction
For each category, I provide links to and a general description of the relevant posts.
If you read and study these, you should gain a solid understanding of the physics of your eyes and how they work.
You will then be more equipped to ask the right questions and make the right decisions regarding any vision impairment corrections you need to make.
I’ll also recommend you take a look at this on-line, free, gem-of-a-book. (“OphthoBook” by Timothy Root MD)
Eye Anatomy
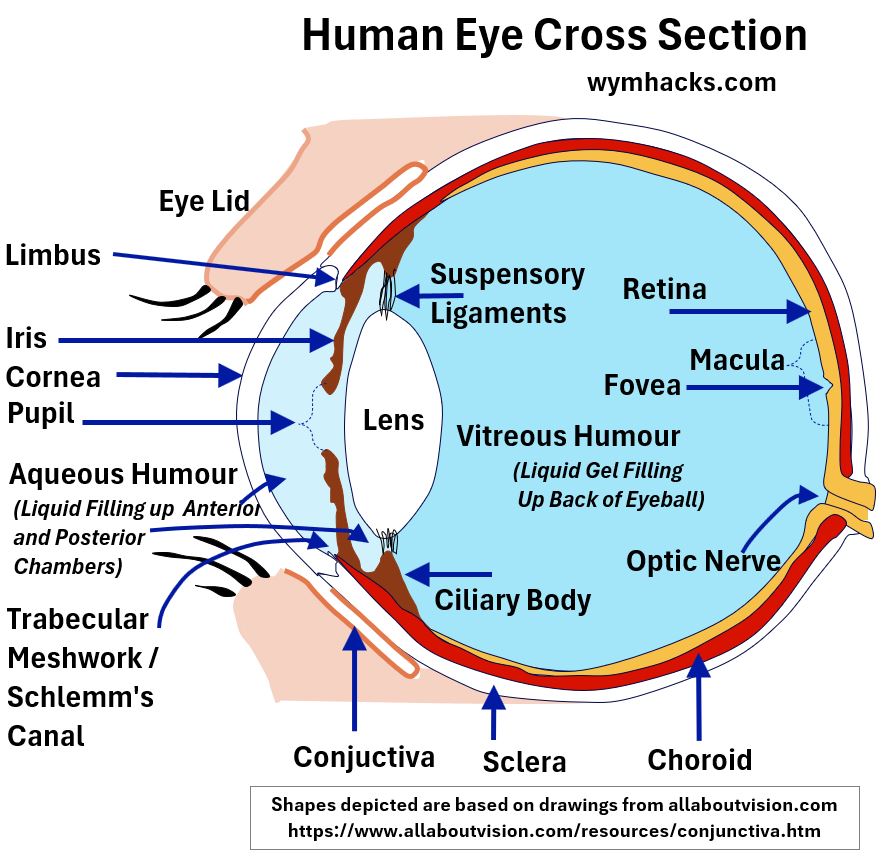
Eye Anatomy
Describes the 10 basic ‘parts’ of the eye and their function
Eye Lens Anatomy
This is the part of the eye that develops cataracts (the lens becomes cloudy and less transparent).
An often used analogy for a lens is an M&M with its
- harder outer candy coat (the Lens Capsule) and
- its inner softer chocolate (the Lens Cortex and Nucleus)
The lens has an important role in focusing images so we can see them clearly.
It actually can adjust via a process called Accommodation.
Light-To-Vision Pathway
A Color Primer (Including How to Create an Effective Colour Palette)
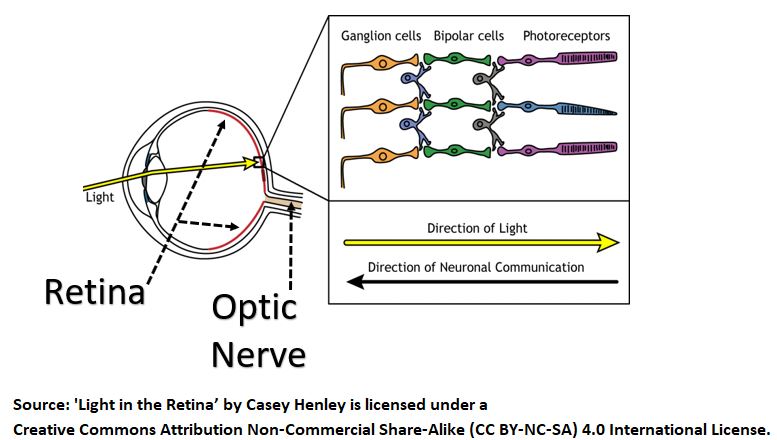
This article describes the light-to-energy pathway in the eye.
I discuss how light (via the Retina and its Cone and Rod photoreceptors) is
- converted into electrical signals and
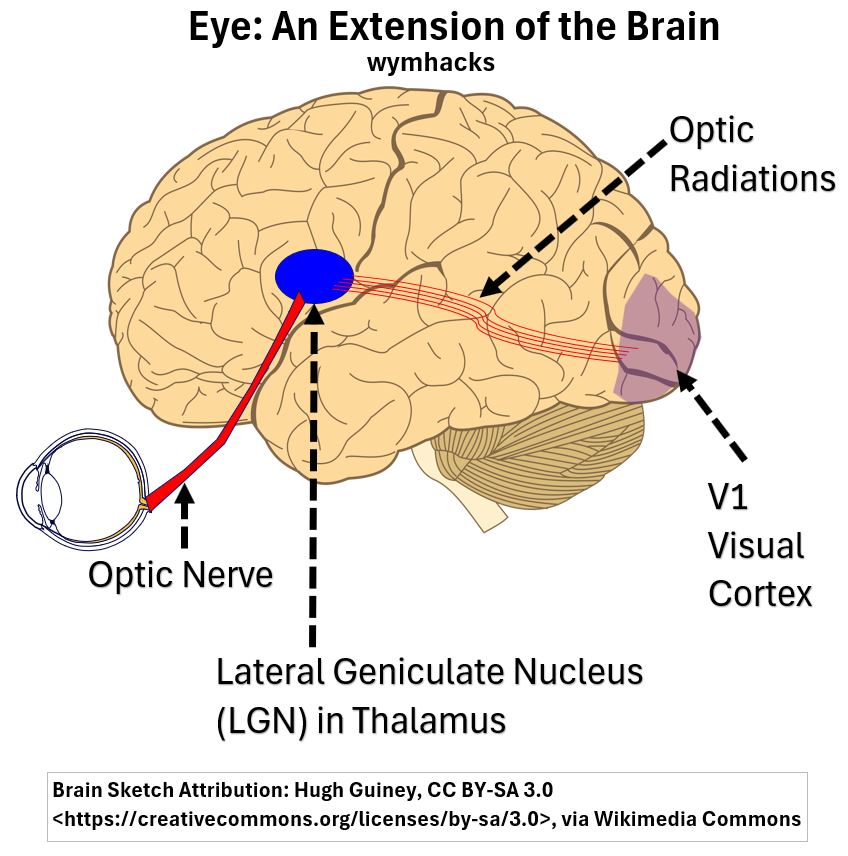
- sent to the brain for final conversion into vision.
Electro Magnetic Radiation
This article explains the fundamental characteristics of light.
Physics of The Eyes
Refractive Geometric Optics
Here I cover eye optics, including
- Ray Theory
- Law of Refraction (Snell’s Law)
- Ray Diagrams
- the Lens Magnification Equation
- the Thin Lens Equation and the
- Lens Maker’s Formula
Lens Ray Diagrams
In this post I describe light converging (convex) and light diverging (concave) lenses and the concept of the Focal Point.
This article
- explains the rules for drawing how light enters and exits the lenses (Ray Diagrams).
- shows several Ray Diagrams (for concave and convex lenses) for Objects located at different locations relative to the lens’s Focal Point.
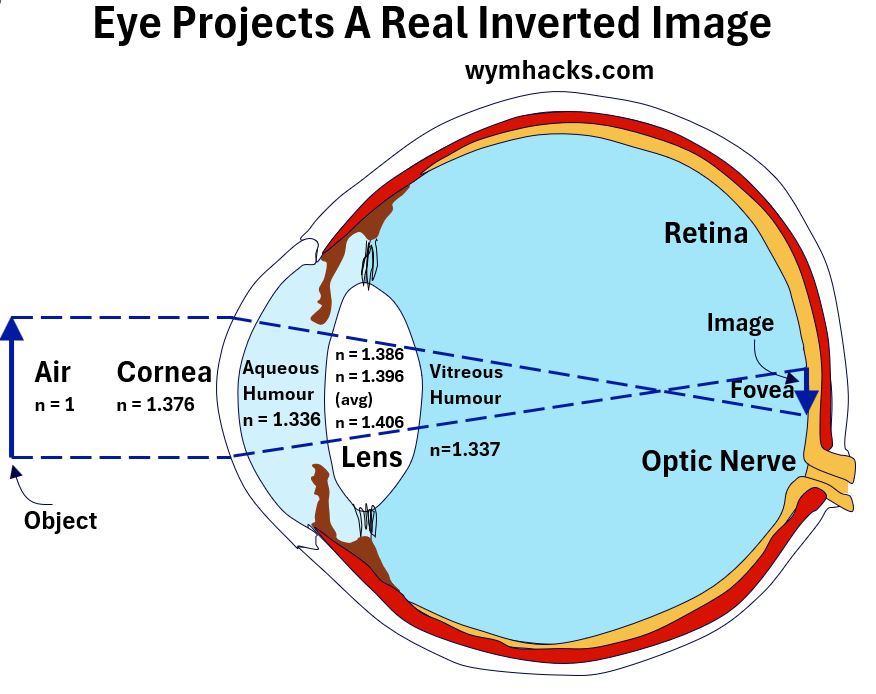
- defines Real Images and Virtual Images
Lens Equations
I show detailed derivations of the Lens Magnification, Thin Lens, and Lens Maker’s equations.
Geometry and Trigonometry Rules
I explain the basic geometry rules that we can use to derive the various lens equations.
Snell’s Law Example – Law of Refraction
I show an example of how Snell’s Law is used to compute light refraction angles.
Light Refraction Tank Analogy
This post provides a useful analogy for the bending and slowing of light rays when light is refracted from a lower refractive medium (e.g. air) to a higher refractive medium (e.g. glass or water).
Wave Superposition
In the Refractive Geometric Optics article, I discuss how light slows down when it goes from air into a medium like glass or water.
Vision Impairment and Correction
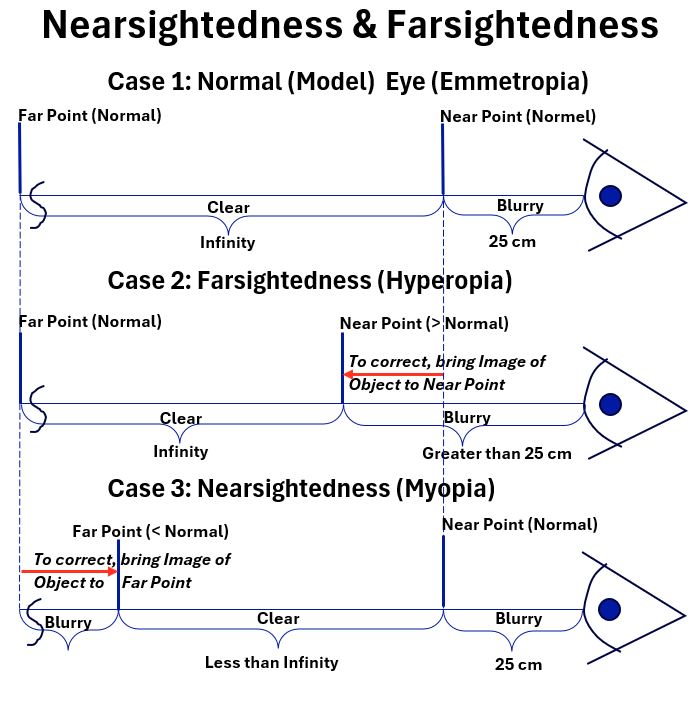
Vision Correction
In this article I review the four types of vision impairment caused by improper focusing of light onto the back of the eyeball (Retina) and describe how they are corrected.
The four Refractive Impairments are
- Nearsightedness (myopia) – distant objects appear blurry
- Farsightedness (hyperopia or hypermetropia) – close objects appear blurry
- Presbyopia – loss of flexibility of the eye lens causes close objects to look blurry (same symptoms as Farsightedness)
- Astigmatism – near and distance objects appear blurry or distorted
Cataracts and Cataract Surgery
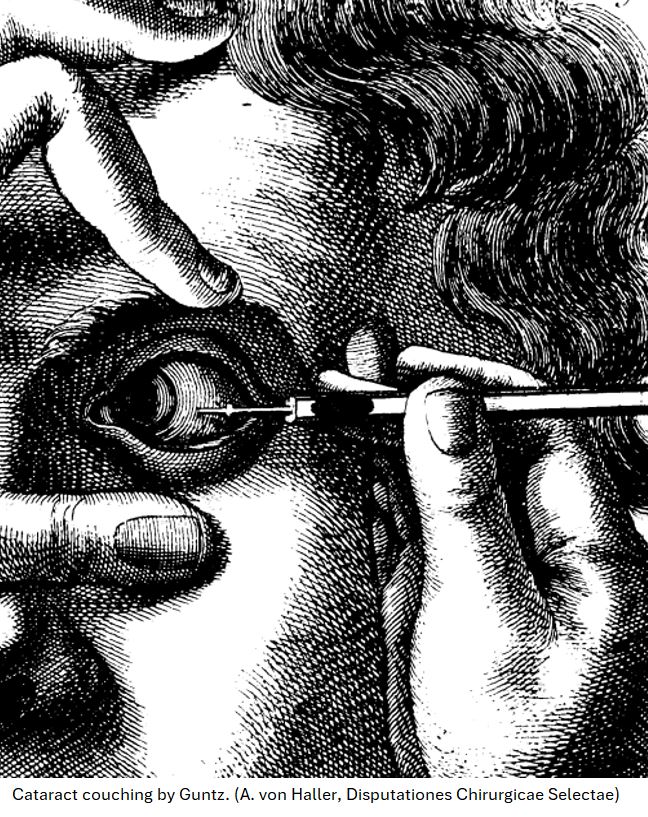
This post covers key things you need to know about cataracts, including
- what they are,
- the history of their treatment (including the ancient practice of couching),
- the characteristics of modern cataract surgery, and
- what to expect before, during, and after the procedure.
Cataract Surgery Tabulated History and References
This post presents a chronological tabulation of cataract surgery through history.
Check out the entertaining description of a cataract “treatment” procedure done thousands of years ago.
Disclaimer: The content of this article is intended for general informational and recreational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional “advice”. We are not responsible for your decisions and actions. Refer to our Disclaimer Page.